The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) regulates interstate transmission and wholesale sales of electricity. Several FERC orders and the Congressional Energy Policy Act of 1992 introduced pivotal changes to the electric power industry.
Passed by Congress in 1992, this landmark legislation promoted competition in the wholesale electric market. One of the Act's provisions amended the Federal Power Act, giving FERC authority to order utilities to provide transmission service to requesting wholesale generators. The Act also promoted the use of solar and renewable energy, overhauled nuclear plant licensing procedures and established programs to increase energy efficiency.
Issued in 1996, these companion orders established the rules regarding opening the nation’s wholesale bulk electric system to competition. These orders required the establishment of an electronic bulletin board called open access same-time information system (OASIS), which allows users to receive data on current operating status and transmission capacity of any transmission provider.
In this order, the FERC encouraged all FERC-jurisdictional utilities that own, operate or control transmission lines (the lines that carry power from generating plants to distribution substations) to turn operational control of those lines over to an independent agency (independent system operator or regional transmission organization).
Learn more about the FERC at www.ferc.gov.
*Source: www.misoenergy.org/AboutUs/History/Pages/History.aspx.

As the only independent grid operator in the western U.S., the ISO grants equal access to 26,000 circuit miles of power lines and reduces barriers to diverse resources competing to bring power to customers. It also facilitates a competitive wholesale power market designed to diversify resources and lower prices.
Every five minutes the ISO forecasts electrical demand, accounts for operating reserves and dispatches the lowest cost power plant unit to meet demand while ensuring enough transmission capacity is available to deliver the power.
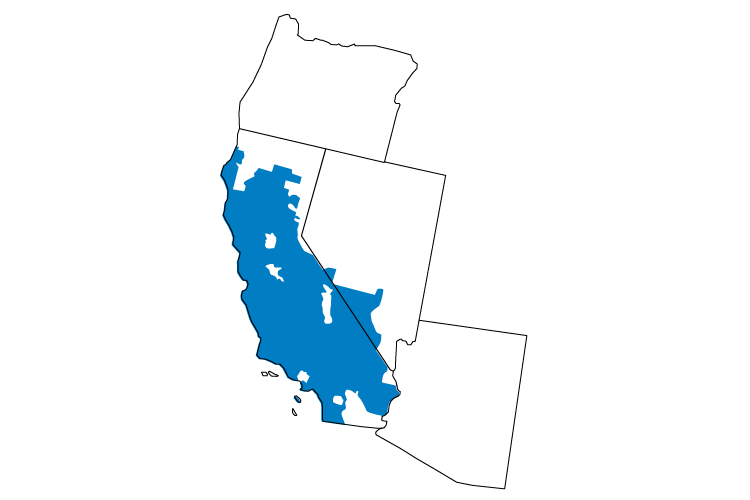
Learn more about the California ISO by visiting www.caiso.com.
The Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) ensures adequate and reliable electrical service to the majority of Texas. It is electrically connected to surrounding areas through DC ties and is therefore not governed by the FERC regulations. While not governed by the FERC, The Public Utility Commission of Texas (PUCT) administers similar market rules and economic factors as in the other markets.
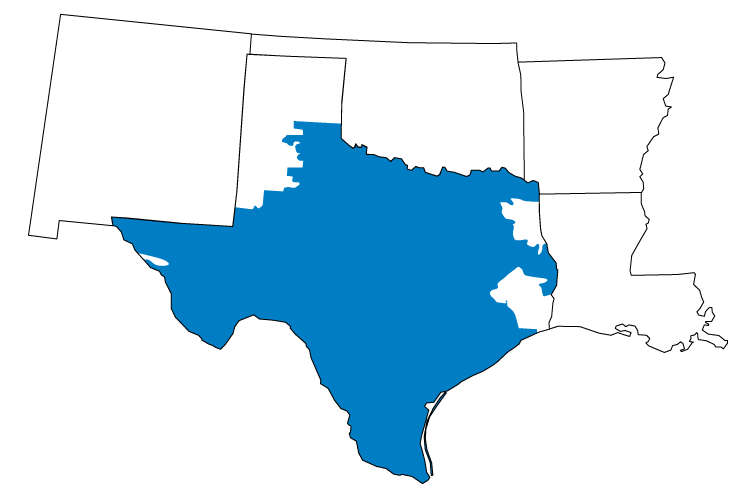
Learn more about the ERCOT by visiting www.ercot.com.

ISO New England is a not-for-profit corporation responsible for keeping electricity flowing across the six New England states and ensuring that the region has reliable, competitively priced wholesale electricity today and into the future.
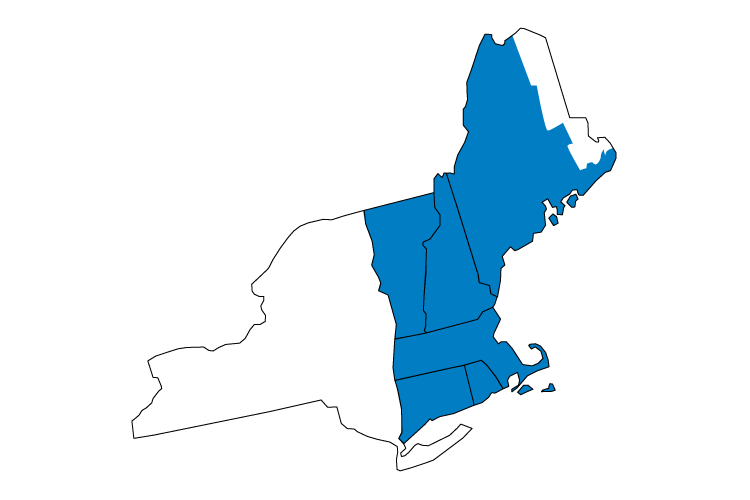
Learn more about ISO New England by visiting www.iso-ne.com.
MISO is an essential link in the safe, cost-effective delivery of electric power across all or parts of 15 U.S. states and the Canadian province of Manitoba. As a Regional Transmission Organization, MISO assures consumers of unbiased regional grid management and open access to the transmission facilities under MISO's functional supervision.
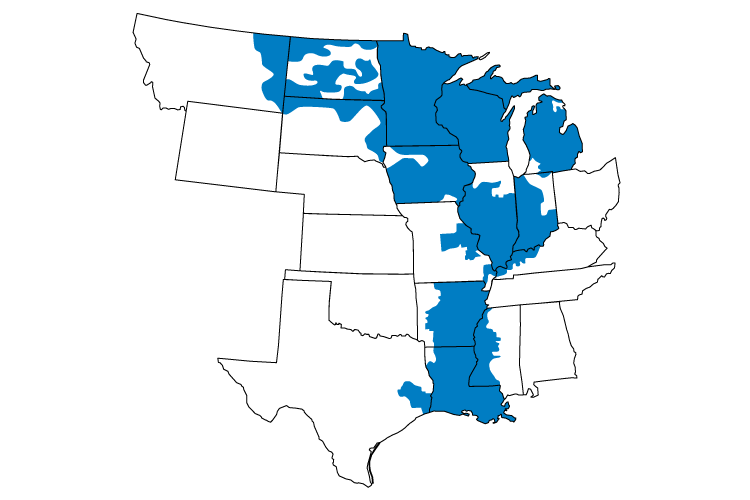
Learn more about MISO by visiting www.misoenergy.org.

The NYISO is responsible for the reliable operation of New York's nearly 11,000 miles of high-voltage transmission and the dispatch of over 500 electric power generators. In addition, the NYISO administers bulk power markets that trade an average of $7.5 billion in electricity and related products annually.
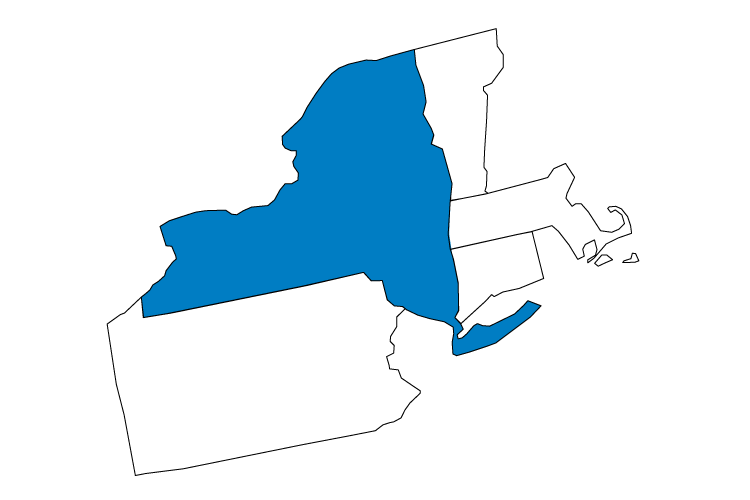
Learn more about the NYISO by visiting www.nyiso.com.

PJM Interconnection is a regional transmission organization (RTO) that coordinates the movement of wholesale electricity in all or parts of Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, New Jersey, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Virginia, West Virginia and the District of Columbia.
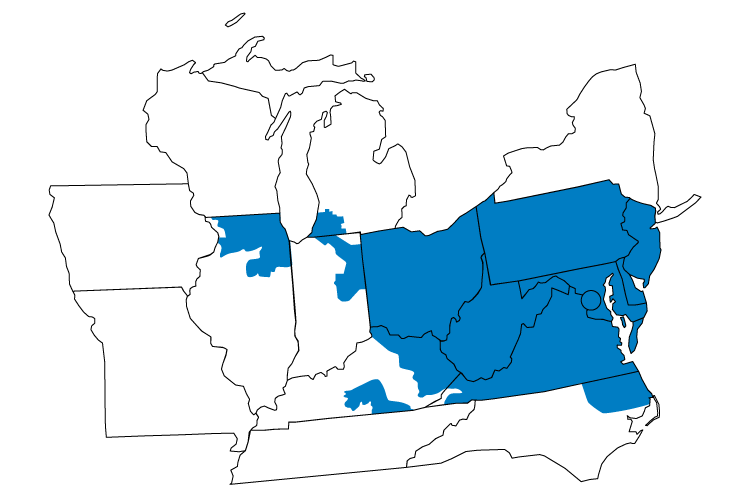
Learn more about PJM by visiting www.pjm.com.

Southwest Power Pool dates to 1941, when 11 regional power companies joined to keep an Arkansas aluminum factory powered around the clock to meet critical defense needs. After the war, SPP's Executive Committee decided the organization should be retained to maintain electric reliability and coordination. After the Northeast power interruption in 1965, other reliability councils were organized.
In 1968, SPP joined 12 other entities to form what became the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC). SPP incorporated as an Arkansas not-profit organization in 1994. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) approved SPP as a Regional Transmission Organization in 2004 and a Regional Entity in 2007.
In North America, SPP is one of nine Independent System Operators/Regional Transmission Organizations (ISOs/RTOs) and one of eight NERC Regional Entities. SPP is mandated by FERC to ensure reliable supplies of power, adequate transmission infrastructure, and competitive wholesale prices of electricity.
ISOs/RTOs are the "air traffic controllers" of the electric power grid. ISOs/RTOs do not own the power grid; they independently operate the grid minute-by-minute to ensure that power gets to customers and to eliminate power shortages.
SPP is based in Little Rock, Ark., and has about 600 employees.
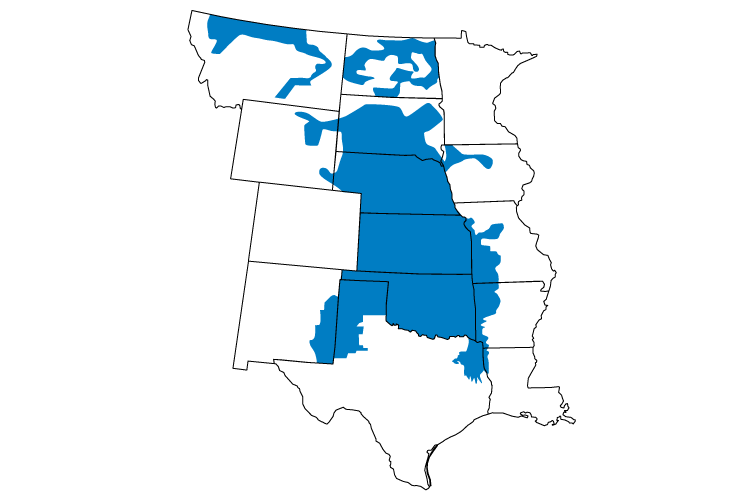
Learn more about SPP by visiting www.spp.org.
Disclaimer: This website is not a solicitation for prospective business, investment or employment. It is intended to provide general information about the companies and to enlighten people about the energy markets and the benefits derived from market participants such as ourselves.
Home | Energy Market Overview | Power Marketers and the Market
© 2024 Monterey Enterprises